General Study Skills Tips
- You need to learn for understanding and long-term recall.
- A proactive, assertive, thought-out, strategic learning strategy is required.
- Don’t try to read or memorize every detail start to finish; such “linear learning” doesn’t work.
- Start with major categories and concepts, and add details.
- Make the material “your own,” think through what’s said in lecture or what you read.
- Strive to understand one topic before going on to the next.
- If you don’t understand something, ask questions in lecture or check with fellow students.
- If a text is confusing, consult with other texts – a different author may be more understandable.
- Adapted from
- Study Without Stress: Mastering Medical Sciences by Kelman & Straker (2000)
- How to Excel in Medical School (3rd ed.) by Saks & Saks (2007)
Strengthening the Student Toolbox: Study Strategies to Boost Learning (John Dunlosky)
- Practice Testing
- Using flash cards or a program like Firecracker are great for practice testing.
- This study strategy may require a lot of work, but in the end it pays off.
- Continual testing is necessary and important for the learning process.
- Answering questions incorrectly on practice tests gives you an indication of what material needs to be restudied.
- Recalling information (versus re-reading material or recognizing information on multiple choice questions) boosts long-term memory.
- Distributed Practice
- Knowledge and skills are better retained when practice is distributed versus massed (e.g. cramming or studying all the material at one point in time).
- Learning may feel tougher when you study in distributed time chunks, but the overall reward is worth it.
- A week or a few days before an exam, blocks of time should be set aside to devote time to studying. This is a strategy to help distribute practice.
Other strategies that show promise are interleaved practice, elaborative interrogation, and self-explanation. Less helpful strategies are highlighting and underlining, summarization, and rereading. Read Strengthening the Student Toolbox to learn more about these study strategies.
Improve your Reading Comprehension
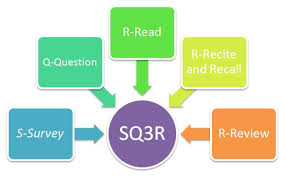
SQ3R is a common strategy used to enhance reading comprehension and thorough study of a topic. SQ3R stands for survey, question, read, recall, and review.
- Survey- Overview the material. Prepare yourself for what you will be learning. Try to anticipate what the author will say.
- Scan the chapter titles
- Read the introduction
- take note of the headings and subheadings
- Recognize the graphics
- Question- Help engage your mind by developing questions pertaining to the material. Try to add questions while you read. Create questions for each topic. This will help boost your interest and focus.
- Read- Read smoothly and with alertness. Look for the answers to your questions and read one section at a time.
- Recall- After each section, recall what you have read. Try to do it without your notes or book. Re-ask yourself your original questions and try to answer them. Try to connect the material you are learning with other material.
- Review- Review your notes frequently but briefly. Before class starts is a prime time to review your notes.
General Study Strategies Video

